SERS
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) uses a surface to enhance Raman scattering. m-oem SERS materials are gold or silver nanoparticles that can be coated on a substrate or suspended in solution. Manufactured with remarkable consistency, our SERS products deliver strong Raman enhancement that is consistent enough to be used for quantitative measurements. No other manufacturer has this combination of enhancement and consistency. Find out what makes m-oem SERS materials unique.
Efficient Analysis at Your Fingertips


Key Benefits:
- Long shelf-life without stringent storage requirements
- High sensitivity and low variability for consistent performance within and across batches
- Easy-to-use: supports diverse methods of sample delivery including dipping, swabbing, and pipetting
- Cost-effective without sacrificing performance
- Customizable form factor to meet diverse application demands
Potential Application Areas Include:
- Illicit drugs detection
- Pesticides identification
- Food and beverage contamination
- Point of Care diagnostics
- Manufacturing QC&QA
- General SERS R&D
Purchase The Discovery Kit
An introductory kit for SERS containing a complete selection of Metrohm’s gold and silver P-SERS strips and gold and silver colloids. This kit can be used to evaluate the suitability of SERS for targeted applications.
Shop SERS Products
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering expands the capabilities of Raman Spectroscopy.
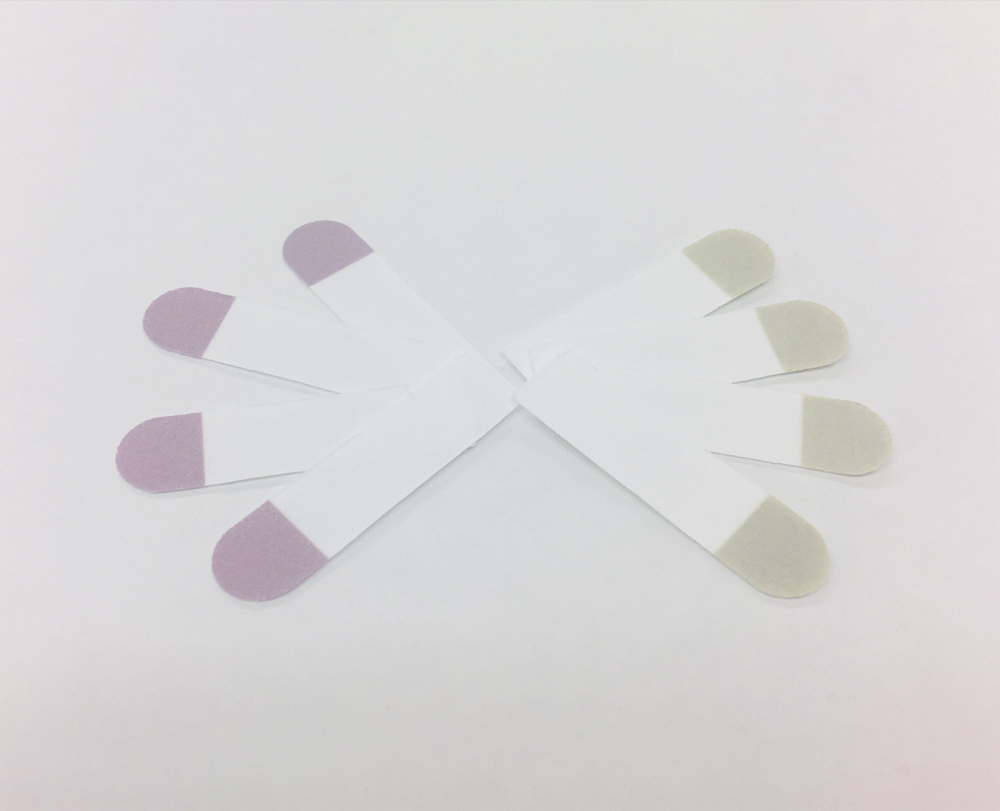
P-SERS Strips
Metrohm’s P-SERS strips are formed using an innovative patented process that deposits nanoparticles via ink-jet printing, dramatically lowering costs while maintaining uniformity and performance.
P-SERS strips can be printed on a variety of porous support materials. Chromatography paper is standard, but the support material can be customized to the application. The properties of the support material
can be leveraged for chromatographic cleanup to enhance detection.
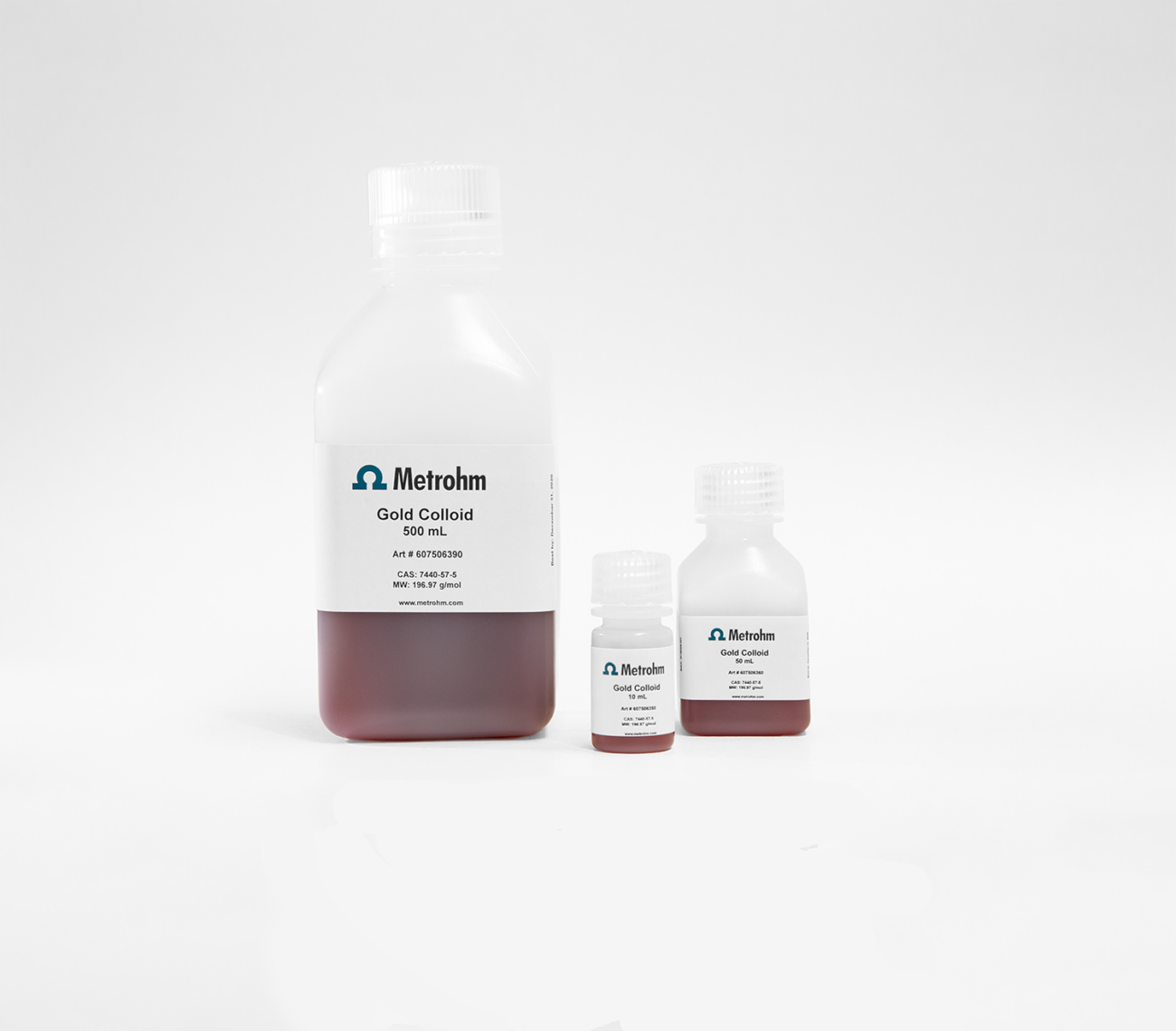
Nanoparticle Colloid Solutions
Poly-dispersed 50 – 200 nm nanospheres are citrate-capped for extended stability. Each batch is fully tested and validated for SERS performance as part of the production process.
Nanoparticles offer high performance in an easy-to-use format.
The sample can simply be mixed with colloidal solution before measurement. A salt solution is often added to induce nanoparticle aggregation and generate SERS hotspots.
